

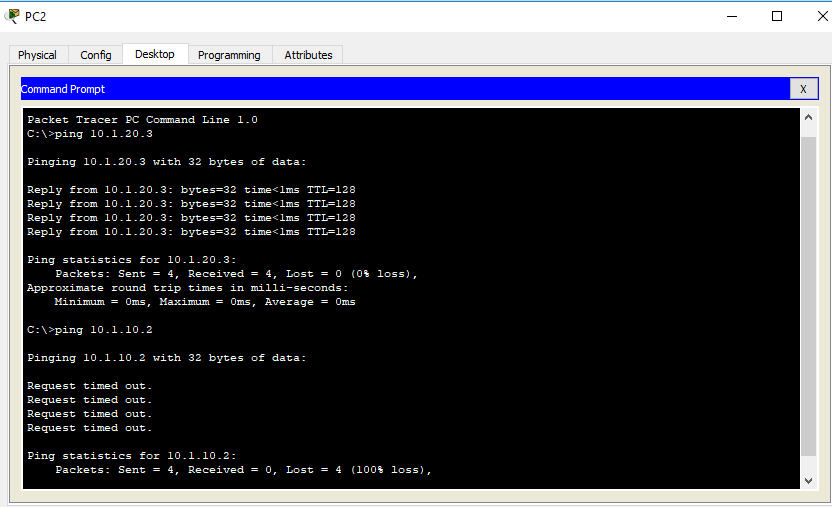
The other devices on the VLAN are sending packets for devices in other VLANs through the router. The subinterface configured for a particular VLAN has an IP assigned from the range of IPs used in that VLAN. The router acts as a Gateway for devices on a VLAN. These switches are called multilayer switches. The switch will handle the Inter-VLAN routing decisions too. However, if your switch is capable of doing Layer 3 functions, you don’t need a router anymore. These subinterfaces have their own IP address and VLAN assignment to be able to operate on a specific VLAN. Subinterfaces are virtual interfaces associated with a single physical interface. To find out more about these encapsulation protocols check the Trunking Concepts lessons from our Cisco CCNA exam preparation series. The protocols used are 802.1Q or Cisco’s proprietary Inter-Switch Link (ISL). Switches are able to recognize the VLAN used for a specific packet through the use of encapsulation protocols that encapsulate or tag the frames. Trunk links are able to accept multiple VLANs on one physical interface. The router is accepting the tagged traffic on the trunk interface and routes it internally using subinterfaces. The router interface is configured as a trunk link and is connected to a trunk switch port. “ Router-on-a-stick” is a type of router configuration in which you are able to use a single physical interface to route traffic between multiple VLANs. In smaller networks this may be enough, but in larger enterprise networks, 48 VLANs may not be enough. This means, you can use that switch to route traffic between VLANs for up to 48 VLANs. A typical switch can have up to 48 ports. Usually, this is not a desired behavior because you end up using too many physical interfaces, and sooner or later you will run out of interfaces. An access mode switch port can belong to only one VLAN and is usually used to connect to an end user device. The switch ports are connected to the router in access mode, and a different static VLAN is assigned to every interface. In classic networks that are using multiple VLANs, routing is performed by connecting multiple physical interfaces on the router to multiple physical interfaces on the switch. The process of forwarding packets from a network to another is called routing and you must use a router to accomplish this.
ROUTER ON A STICK CONCEPT HOW TO
They belong to different networks, different broadcast domains and switches do not know how to forward packets from one network to another. A host belonging to a VLAN attached on a specific physical port, for example VLAN 10 in port FastEthernet0/10 is usually not able to communicate to a host attached to another VLAN, for example VLAN11 attached to port FastEthernet0/11.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
